What is Leukoplakia?
 The term Leukoplakia doesnt describe a specific disease but a clinical observation. Clinically Leukoplakia looks like a white patch which cannot be removed. It can have different surfaces such as smooth, fissured, varicous or speckled. Risk factors of Leukoplakia are the “6 s”
The term Leukoplakia doesnt describe a specific disease but a clinical observation. Clinically Leukoplakia looks like a white patch which cannot be removed. It can have different surfaces such as smooth, fissured, varicous or speckled. Risk factors of Leukoplakia are the “6 s”
– smoking
– spirit
– sharp tooth( traumatic origin)
– spicy food
– syphilis
– sepsis( specifically candida infection and human papilloma virus).
Beside the etiological factors above a Vitamin A deficiency can cause a Leukoplakia as well.
Leukoplakia can be differentiated in 4 clinical stages based on its size an 5 stages based on its histopathological status which are:
– no dysplasia
– mild dysplasia
– moderate dysplasia
– severe dysplasia(with high risk to be transformed to oral cancer)
– squamous cell carcinoma in situ with a poor prognosis and high letality

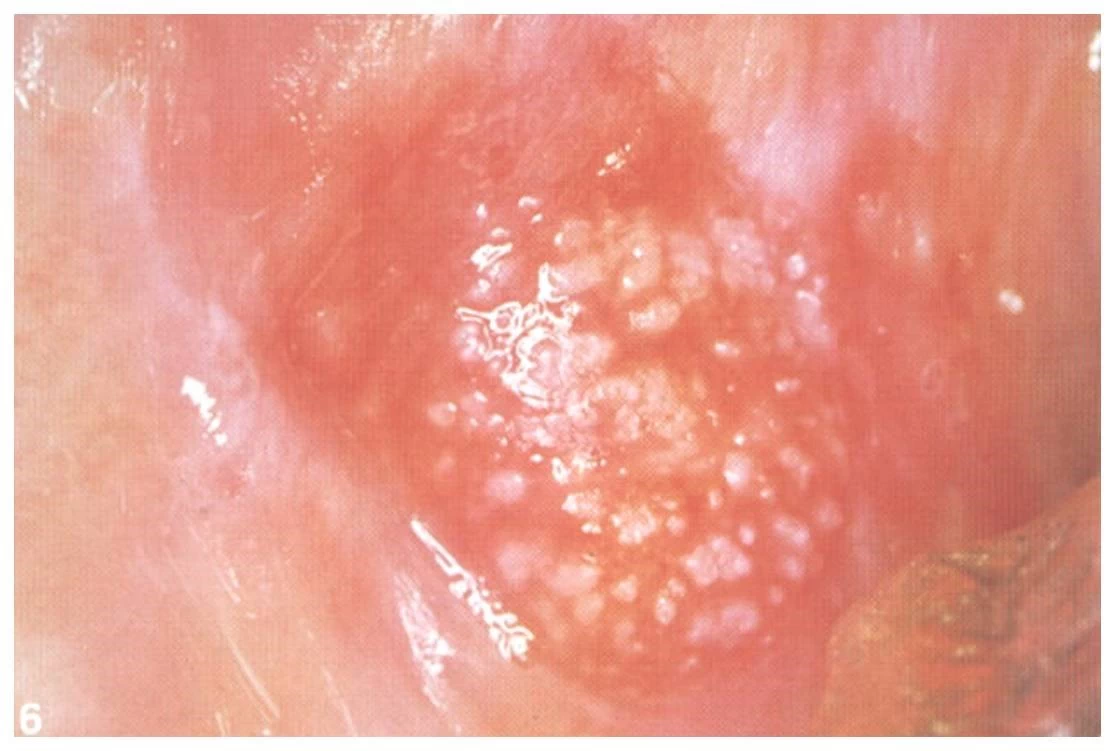
The surface of Leukoplakia can vary not only in its size but as well in its clinical appearance which could be :
-smooth
-fissured
-verruciform
-speckled
picture different surfaces
A biopsy would be needed in case a leukoplakia is detected as the following lesions look similar:
– White spongus nevus
– Lichen planus
– Acute pseudomembranous candida albicans
– Morsicatio buccarum
– Leukoedema
Leukoplakia can be treated by non surgical approach is:
-Vitamin A
-Vitamin E
-Vitamin C
or others.
Then the invasive approach could be performed by
-Cryotherapy
-Carbon dioxide or Erbium Yag Laset therapy(Excision or Vaporization)
-Electrocautery
-Surgical excision
Always watch out for uncommon appearances in your mouth as they can be related to serious conditions like oral cancer or other systemic diseases.




